
LCD Display vs. OLED: Which is Right for You?
Which one reigns supreme? Is it LCDs or OLEDs?
The battle for superior display technology rages between Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) and Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED). There’s is a longstanding rivalry in the display technology world. Both formats have champions and detractors, each offering distinct advantages and drawbacks.
This article delves into the key differences between these two display types and their strengths and weaknesses, helping to understand which technology best suits one’s needs. From picture quality and energy efficiency to cost and durability, we’ll break down the factors that matter most.
1. What are LCD and OLED Displays?
LCD is a display technology that uses liquid crystals to control the amount of light that passes through the screen. It requires a backlight to illuminate the pixels.
OLED is a display technology where each pixel can produce its light. OLED displays don’t require a backlight and can achieve deeper blacks and better contrast ratios.
Understanding the differences between the two is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. These technologies offer distinct advantages in terms of picture quality, viewing angles, and energy efficiency. By knowing their strengths and weaknesses, consumers can select the display that best suits their needs and preferences.
2. LCD Display vs. OLED Parameter Comparison
What’s the Picture Quality?
When comparing LCD and OLED displays, picture quality stands out as a critical factor. OLEDs are praised for their deep black levels, which significantly improve contrast. This is possible because each pixel in an OLED display can be independently turned off, creating true blacks and exceptional detail in dark scenes. In contrast, LCDs rely on a backlight to illuminate their pixels, often resulting in lighter blacks and reduced contrast.
When it comes to motion handling, OLED displays have a clear advantage. They have faster response times to display fast-moving content with minimal motion blur, making them ideal for watching sports or playing video games. LCDs, on the other hand, can struggle with motion blur due to slower pixel response times. While technologies like LED backlighting and motion smoothing can somewhat mitigate this issue, they can’t quite match the crisp, smooth motion that OLED displays provide.
What’s the Color Accuracy?
OLED and LCDs differ in terms of color accuracy. OLEDs produce accurate black levels, which leads to higher contrast and more vibrant colors.
In contrast, LCDs use a backlight to illuminate pixels, which can make colors less accurate, especially in darker areas. However, high-quality LCDs with technologies like Quantum Dot can come close to OLEDs in color accuracy. Overall, OLEDs usually have the edge in color accuracy due to their unique pixel lighting method.

What’s the Energy Efficiency?
Energy efficiency is an important factor to consider. OLEDs are often seen as more efficient because they light up only the pixels needed for an image. This means darker images use less power, making OLEDs more efficient in certain situations. However, if most of the content is bright or white, OLEDs can use more energy since all the pixels need to be lit.
On the other hand, LCDs use a constant backlight to illuminate their pixels, so their power use stays relatively stable regardless of what’s on the screen. This can make them less efficient for darker images than OLEDs, but they might be more efficient for brighter or white images. Other factors like screen size and resolution can also affect the energy efficiency of both display types.
What’s the Contrast Ratio?
Contrast ratio is the difference in luminance between the brightest white and the darkest black a display can produce, indicating image clarity and depth.
Contrast ratio plays a crucial role in display technology and dramatically affects the viewer’s experience.
OLED displays are famous for their ability to deliver infinite contrast ratios. Each pixel in an OLED can be individually lit, allowing for true blacks when pixels are completely turned off. This produces more vibrant and lifelike image quality, especially in dark scenes or low-light environments.
Additional points:
● OLED displays can achieve infinite contrast ratios.
● True blacks are possible with OLED technology due to the ability to turn off individual pixels.
● OLED’s contrast ratio adds vibrance; the image has a life-like quality.
Meanwhile, LCDs rely on a backlight to illuminate their pixels, which prevents them from achieving true black due to some light leakage. As a result, compared to OLEDs, LCDs usually have lower contrast ratios. Although advancements like Full-Array Local Dimming (FALD) have improved their contrast ratios, they still can’t match the infinite contrast OLED offers.
Additional points:
● LCDs have lower contrast ratios due to backlight illumination.
● True black is not achievable on LCDs due to light leakage.
● Despite advancements like FALD, LCD contrast ratios still fall short of OLEDs.
3. LCD Display vs. OLED Application Comparison
Is there a Price Difference?
OLED displays typically cost more compared to LCD screens. OLED displays tend to carry a premium price tag due to the complex manufacturing process that involves specialized materials. Nevertheless, their exceptional color accuracy, deep blacks, and faster response times often justify the higher cost for consumers seeking top-tier visual performance.
LCDs have a more extended history and benefit from a more established manufacturing process, lowering production costs. This affordability makes them a popular choice for budget-conscious consumers. While offering decent image quality, LCDs generally need more OLEDs regarding contrast and color accuracy. However, they are known for their durability and resistance to burn-in, making them a reliable option for long-term use.
Which is More Eco-friendly?
The environmental impact of display technology is a growing concern. The good news is that both LCD and OLED have pros and cons regarding eco-friendliness.
OLED displays have a potential edge in terms of energy efficiency. Since they can turn off individual pixels for black sections, they can consume less power compared to LCDs, which require a backlight constantly running. Additionally, OLEDs have shown promise in recyclability, with some manufacturers claiming higher recycling rates for their components.
Due to their backlight, LCDs have traditionally been more energy intensive. However, advancements in LED backlighting technology have improved efficiency. While recycling rates are generally reasonable, the complexity of LCD panels can pose challenges in this area.
Overall, environmental impact depends on various factors, including manufacturing processes, energy sources used, and end-of-life management. While OLEDs currently seem to have a slight edge in terms of energy efficiency and recyclability, the landscape is constantly evolving.
Both technologies are undergoing continuous improvements to reduce their environmental footprint. Ultimately, the most eco-friendly choice depends on various factors, including the specific product, usage patterns, and disposal methods.
Which One has Better Brightness?
A critical distinction between OLED and LCDs lies in their backlight systems. LCDs employ an LED backlight to illuminate the entire screen, while OLEDs generate light directly from each pixel. This fundamental difference impacts brightness.
OLEDs excel at pixel-level brightness, delivering intense, vibrant colors. However, the absence of a dedicated backlight can limit overall screen brightness.
LCDs, on the other hand, consistently offer higher overall screen brightness thanks to their powerful backlights. While individual pixel brightness might not match OLEDs, LCDs produce a brighter picture across the entire display.
How is the Life Span?
LCDs have a proven track record. With years of data available, they’re estimated to last around 60,000 hours or roughly seven years of consistent use. While backlight dimming can occur over time, it typically doesn’t significantly impact image quality.
OLED displays are relatively new to the market, making long-term data limited. Current projections estimate a lifespan of 100,000 hours or about ten years of consistent use. However, OLEDs are susceptible to burn-in, where static images can leave permanent marks. While mitigated by recent advancements, this risk is still a factor to consider.
4. What's the Best Choice?
The LCD versus OLED debate often comes down to individual priorities. LCDs offer a solid option if budget, energy efficiency, and durability are key factors. However, those seeking exceptional picture quality, with deep blacks and vibrant colors, will likely lean towards OLED.
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer, and LCD and OLED technologies continue evolving. Rely on your personal needs or Seel expert advice before choosing.
Did you know that Rental LED displays offer a flexible and cost-effective solution for events, conferences, and outdoor promotions? These large-scale screens can be customized to fit various spaces and provide high-impact visuals for any audience.
Check out the LEDSINO RX-Series here.
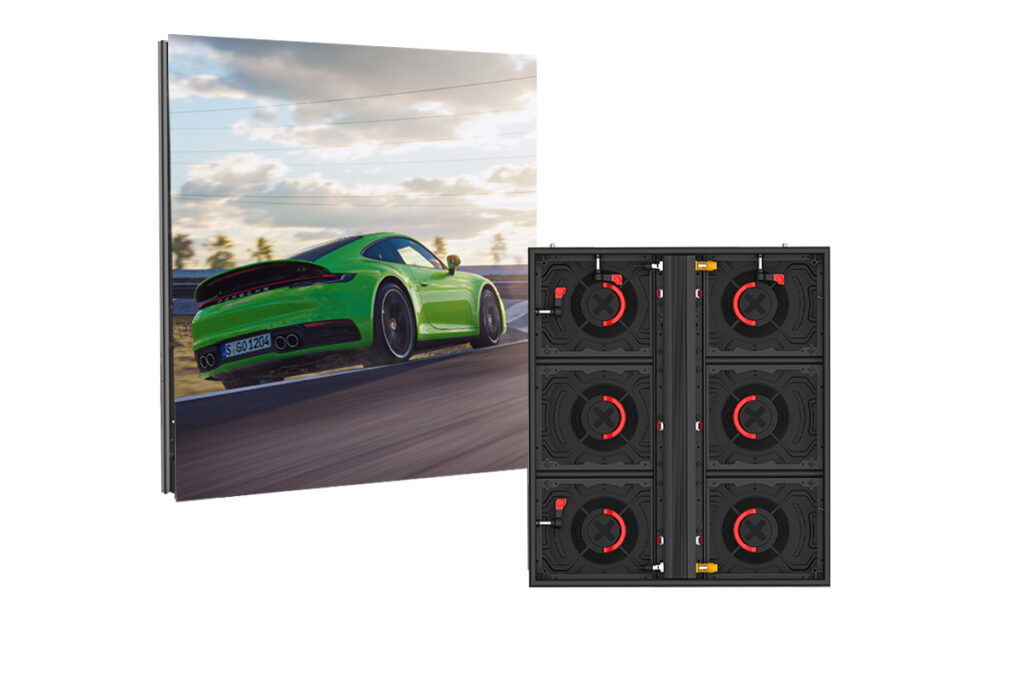

- Energy Saving Display 30% Design
- Standard Modules Front/Rear Service
- Size: 400*300mm/800*900/1200mm
- Display Can Operate at -30°C to 60°C
- With 3 Years Warranty and 5% Spare Parts
5. Final Thoughts
As technology continues to advance, there is a gap between OLEDs and LCDs. This gap makes deciding which one to buy even more complex. Ultimately, the best way to determine which display is correct is to experience firsthand and consider your specific needs and budget.